About Samsung Company : A Global Leader in Innovation and Technology
Samsung is a name that resonates with quality, innovation, and technological excellence across the globe. What started as a small trading company in South Korea has grown into one of the world’s leading conglomerates, with a significant impact on the global electronics, construction, shipbuilding, and financial sectors. The name “Samsung” means “three stars” in Korean, symbolizing something big, powerful, and everlasting—and the company has certainly lived up to that ambition.
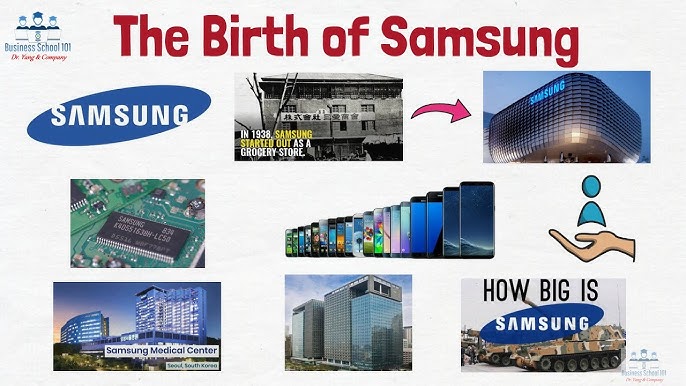
History and Evolution
Samsung was founded by Lee Byung-chul in 1938 as a trading company dealing in dried fish, locally-grown groceries, and noodles. It wasn’t until the late 1960s that Samsung entered the electronics industry. Its first products included black-and-white televisions, and by the 1970s and 1980s, Samsung had expanded into home appliances, telecommunications, and semiconductors.
The 1990s marked a turning point for Samsung as it began to invest heavily in design, quality control, and international marketing. Under the leadership of Lee Kun-hee, the founder’s son, Samsung adopted a new philosophy: “Change everything except your wife and children.” This bold approach led to a major transformation in corporate culture, and the company began focusing more on innovation and brand development.
Business Divisions
Samsung operates as a chaebol—a large family-controlled conglomerate unique to South Korea. It has numerous affiliated businesses, but the most prominent and globally recognized is Samsung Electronics, which contributes a significant portion of the group’s revenue.
Some of Samsung’s major business divisions include:
- Samsung Electronics: The crown jewel of the conglomerate, producing smartphones, televisions, semiconductors, home appliances, and display panels. It’s one of the world’s largest producers of mobile phones and memory chips.
- Samsung Heavy Industries: A major player in shipbuilding, known for building some of the world’s largest container ships and oil rigs.
- Samsung Engineering & Construction: Involved in building landmarks such as the Burj Khalifa in Dubai and various infrastructure projects globally.
- Samsung Life Insurance: A leading life insurance company in South Korea, reflecting the conglomerate’s strong presence in financial services.
- Samsung SDS: Provides IT services, including cloud computing, AI, and cybersecurity solutions.
Innovations and Technology Leadership
Samsung is renowned for its innovations, particularly in the smartphone and semiconductor sectors. The company spends billions of dollars annually on research and development (R&D), helping it stay ahead in the competitive tech industry.
Some of Samsung’s landmark innovations include:
About samsung company
- Galaxy Series: Samsung’s flagship line of smartphones has been one of the strongest competitors to Apple’s iPhone. The Galaxy Note introduced the concept of the “phablet,” while the Galaxy Z Fold series showcases Samsung’s leadership in foldable display technology.
- Semiconductors: Samsung is one of the top producers of DRAM, NAND flash memory, and processors, supplying not just its own devices but also competitors and partners around the world.
- Display Technology: The company leads in AMOLED and OLED display technologies, used in smartphones, TVs, and wearables.
- 5G and AI: Samsung has made significant investments in next-generation mobile networks and artificial intelligence to shape the future of connectivity and computing.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite its success, Samsung has faced several challenges:
- Legal and Ethical Issues:
Samsung has been involved in various legal battles, most notably with Apple over smartphone patents. In 2017, Samsung’s vice chairman Lee Jae-yong was arrested and later convicted in a high-profile bribery scandal that shook South Korea’s political and corporate landscape. - Product Failures:
The Galaxy Note 7 debacle in 2016, where devices were prone to catching fire due to battery defects, damaged the company’s reputation temporarily. Samsung responded with rigorous quality control measures and regained consumer trust through transparent communication. - Global Competition:
Samsung faces stiff competition from Chinese manufacturers like Xiaomi, Huawei, and Oppo, especially in emerging markets. In premium segments, Apple remains its primary rival. - Geopolitical Tensions:
As a global company, Samsung is impacted by trade tensions, especially between the U.S. and China. Semiconductor export controls and supply chain disruptions have become significant strategic concerns.
Samsung and the Future
Samsung is actively investing in next-generation technologies like:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 6G communication
- Quantum computing
- Advanced semiconductor manufacturing
- Smart cities and digital health
Samsung also plans to become carbon neutral by 2050, with increased investments in renewable energy and eco-friendly products. Its SmartThings platform aims to integrate home automation, AI, and IoT for smarter living environments.
In 2023, Samsung announced a $230 billion investment plan over the next20 years to build the world’s largest semiconductor hub in South Korea.
Conclusion
Samsung’s journey from a small trading company to a global tech titan is a story of bold vision, adaptability, and relentless innovation. Despite the occasional controversy or market challenge, Samsung has consistently pushed the boundaries of technology, influencing how people communicate, work, and live. With a strong commitment to research, sustainability, and digital transformation, Samsung is well-positioned to continue shaping the future of technology for decades to come.ee
People also read:Home