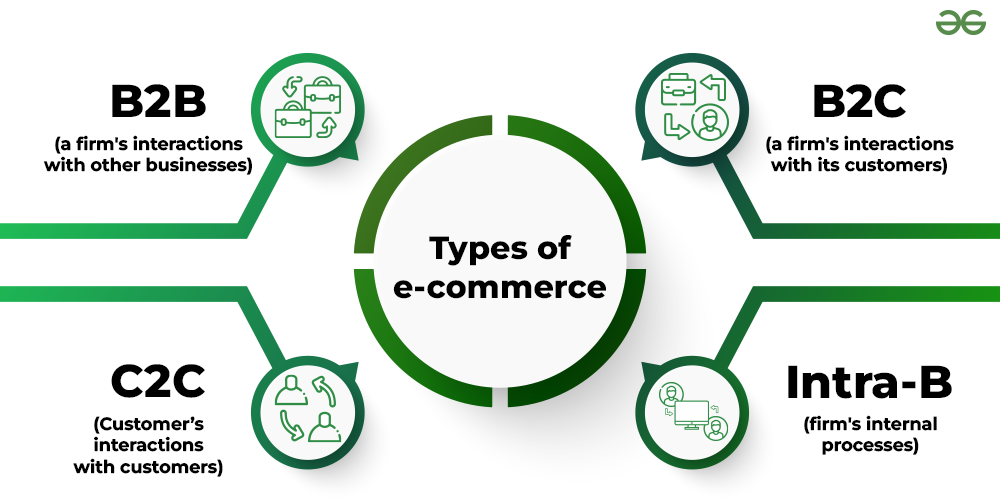
E-commerce refers to commercial transactions conducted electronically over the internet. It includes a variety of data, systems, and tools for online buyers and sellers, including mobile shopping and online payment encryption. There are several types of e-commerce, including:
- B2C (Business to Consumer): Businesses sell directly to consumers, such as Amazon, Flipkart, or Zalando.
- B2B (Business to Business): Businesses sell to other businesses, such as Alibaba or industry-specific platforms.
- C2C (Consumer to Consumer): Consumers sell to each other, often through platforms like eBay or Facebook Marketplace.
- C2B (Consumer to Business): Individuals sell goods or services to businesses, like freelancers on platforms such as Fiverr or What
What is E-Commerce?
The Growth of E-Commerce
The rise of e-commerce can be attributed to several technological and social factors. The widespread availability of the internet, the development of smartphones, and improvements in online payment systems have all contributed to the explosive growth of online shopping. According to various industry reports, global e-commerce sales are projected to reach over $6 trillion by 2025, making up more than 20% of total global retail sales.
This growth accelerated significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic, as lockdowns forced consumers to turn to online platforms for both essential and non-essential purchases. Even post-pandemic, consumer habits have shifted, with many preferring the convenience and variety offered by online shoping.
Key Benefits of E-Commerce
E-commerce offers several advantages for both businesses and consumers:
- Global Reach: E-commerce breaks down geographical barriers, allowing businesses to reach customers worldwide without the need for physical stores.
- Lower Operational Costs: Running an online store generally requires less capital investment compared to brick-and-mortar outlets.
- Convenience: Consumers can shop 24/7 from the comfort of their homes, compare prices, read reviews, and make informed decisions.
- Personalization: Online stores can use customer data to personalize the shopping experience, offer recommendations, and tailor marketing strategies.
- Scalability: E-commerce businesses can scale more easily and rapidly, adding new products, services, or markets with relatively low overhead.
Challenges in E-Commerce
Despite its advantages, e-commerce also comes with its own set of challenges:
- Competition: The low barrier to entry means many businesses enter the market, making it highly competitive.
- Logistics and Delivery: Managing inventory, shipping, and returns can be complex, especially for global operations.
- Security: Online transactions are susceptible to cyber threats, necessitating robust security measures.
- Customer Trust: Building trust online can be harder without face-to-face interaction. Poor service or negative reviews can quickly harm a business’s reputation.
- Technical Issues: Downtime, payment gateway errors, or a poorly designed website can result in lost sales and a negative user experience.
- What is E-Commerce?
Trends Shaping the Future of E-Commerce
Several key trends are shaping the evolution of e-commerce:
- Mobile Commerce: With the rise of smartphones, mobile shopping is becoming increasingly important. Businesses must optimize their websites and apps for mobile users.
- Social Commerce: Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook are becoming integral to the shopping journey, allowing users to shop directly through social media.
- Voice Commerce: Smart assistants like Amazon’s Alexa and Google Assistant are enabling voice-activated shopping, creating a new channel for e-commerce.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI is revolutionizing e-commerce through chatbots, personalized recommendations, inventory management, and fraud detection.
- Sustainability: More consumers are demanding environmentally responsible practices. E-commerce companies are responding with eco-friendly packaging, ethical sourcing, and carbon-neutral shipping.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR helps consumers visualize products in their space before purchasing, especially in fashion and furniture sectors.
- What is E-Commerce?
How to Start an E-Commerce Business.
Launching an e-commerce business requires careful planning and strategy. Here are the basic steps:
- Identify a Niche: Choose a product or service that addresses a specific customer need or solves a problem.
- Conduct Market Research: Understand your competitors, target audience, and pricing strategies.
- Choose a Business Model: Decide whether you’ll hold inventory (traditional e-commerce), use dropshipping, or offer digital products/services.
- Build an Online Store: Use platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, or BigCommerce to create your website.
- Set Up Payment and Logistics: Partner with secure payment gateways and reliable shipping providers.
- Market Your Store: Use SEO, social media marketing, email campaigns, and influencer partnerships to drive traffic and sales.
- Optimize Continuously: Analyze customer behavior, feedback, and sales data to refine your strategies and improve the shopping experience.
What is E-Commerce?
Conclusion
E-commerce is not just a passing trend — it’s the future of retail. As technology continues to evolve and consumer expectations shift, businesses must adapt or risk being left behind. With lower entry costs and the ability to reach a global audience, e-commerce presents an exciting opportunity for entrepreneurs and established businesses alike. However, success in this space requires a customer-centric approach, strong digital infrastructure, and continuous innovation. As we look ahead, those who can blend convenience, personalization, and trust will dominate the e-commerce landscape